CONQUERING MALARIA
CONQUERING MALARIA: A brief summary on what you should know about it.
Malaria affects millions of people particularly young children under the age of 5, Pregnant women, HIV/AIDS patients and people with no prior experience to malaria. This is why the importance of learning about the body and its potential threats cannot be overemphasized. So that brings us to the question; WHAT IS MALARIA?
We have always heard that mosquito bites are the root cause of malaria, but that information is not completely accurate. You see mosquitoes do not cause malaria but spread them, the actual cause of malaria is the plasmodium parasite. These are single cell parasites that get spread by mosquitoes.
HOW DOES ONE GET MALARIA? 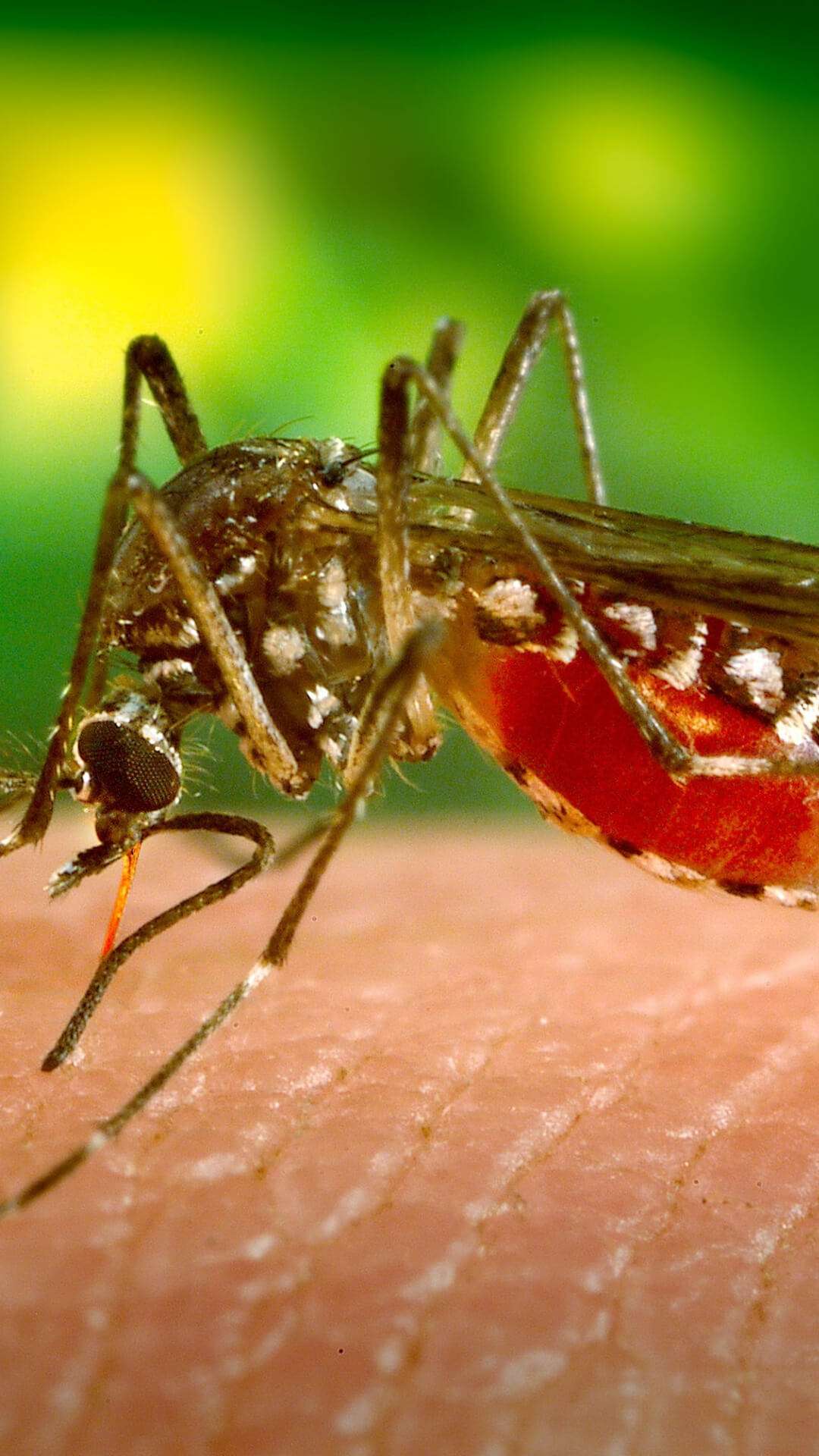
There are many species of plasmodium but only 5 have been identified to cause diseases in humans
1. Plasmodium falciparum (most violent)
2. Plasmodium vivax (widespread and often causes relapsesof malaria due to its ability to remain in the liver).
3. Plasmodium ovale (less common but similar to vivax)
4. Plasmodium malariae (milder and can persist in the bloodstream for years)
5. Plasmodium knowlesi (mainly affects monkeys but can also affect humans)
HOW CAN ONE PREVENT MALARIA
Preventing malaria involves a combination of measures to reduce exposure to mosquitoes and to protect against infection. Here are some key strategies for malaria prevention:
1. USE MOSQUITO BED NETS: sleep and a mosquito bed net treated with insecticide especially in areas where malaria is prevalent. This provides a physical barrier against mosquito bites while the insecticide helps repel and kill mosquitoes.
2. Apply insect repellent: use insect repellent containing DEETS and other EPA approved ingredients on exposed skin and clothings to repel mosquitoes.
3. Take antimalarial medication: if travelling to an area with malaria consult with a healthcare provider about taking antimalarial medication as a preventative measure. The choice of medication will depend on the destination and individual factors such as medical history and allergies.
4. Seek early diagnosis and treatment, be aware of the symptoms of malaria such as fever, chills, headache, and body aches, and seek prompt medical attention if you develop symptoms after travelling to malaria endemic area.
5. Eliminate mosquito breeding sites; Reduce standing water around your home, such as in containers, flowerpots, and the gutters, to prevent mosquitoes from breeding.
6. Protect vulnerable population; take extra precautions to protect pregnant women, young children, and other vulnerable individuals who may be at a higher risk of severe malaria.
By following these preventive measures, you can greatly reduce your risk of contracting malaria while travelling to or living in areas where the disease is endemic. For more enquiries on where to get professional medical healthcare services Contact Us Today

Leave a comment